Often, when we talk with customers, they ask how PROFINET compares with other network protocols. In this article, we’ll explain how PROFINET and Modbus TCP compare head to head in order to help you understand the differences between them. At the end of the comparison, we’ll show a table highlighting the main points for quick reference.
Speed and Determinism
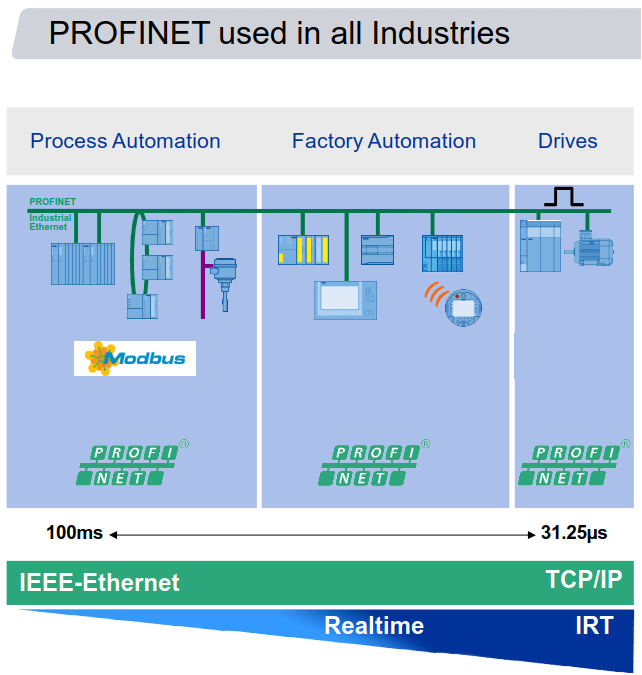
When it comes to a comparison of speed and determinism, PROFINET is the clear winner. PROFINET uses Ethernet for real time data exchange with a provider/consumer model whereas Modbus uses TCP/IP with a client/server model. You may ask what is big deal with that? Well, one is the fact that Modbus TCP uses half duplex communications at Layer 4 of the OSI model while PROFINET uses full duplex at Layer 2. Half duplex is a request/reply or ‘polling’ type of communication that makes the communication slow and laborious. A client must first send a request to a server, then the server answers this request for every transaction. In addition, Modbus TCP packs its IO data and wraps it inside of a TCP/IP message, which makes transfer time longer. With PROFINET IO full duplex, each device sends its data on its own without waiting for the partner thereby taking advantage of the Ethernet standard. This is handled by each device being a provider of data, and a consumer of data at the same time, the controller sends the output data, devices send inputs.
Speed is also quite fast with PROFINET as typical IO devices can run at 1ms update times with minimum cycle times from the standard of 31.25uS with the fastest motion control devices. During testing, this speed is monitored and cannot deviate outside allowed tolerances. (ex: 10% above allocated time) With Modbus TCP, there is not a specified performance factor, and there is no specified timing for this process and the handshaking mechanisms.
Application Breadth Comparison
When it comes to application breadth PROFINET can work for factory, process, and motion control applications simultaneously from the most simple, to the most complex. Modbus TCP is typically used with process applications because the timing is not critical, but you have to be more careful when planning for factory automation. Also, it does not support high-speed motion control.
Programmed vs Configured Communications
Modbus TCP is a programmed communication which has to be set up in the PLC code via programming function, block, or tool. PROFINET is a configured communication, and only in special cases would require programming in code (e.g. isochronous motion control). Each PROFINET vendor provides a general station device description (GSD) of their device which is used to bring in the device in order to configure it in the engineering tool. This makes setup much easier than having to write special PLC code or setup blocks just for the communications.
Data Representation
Modbus has two data types for data representation: a coil (bit) or or a register (word). PROFINET has many forms of data representation including bits, bytes, words, doublewords, real numbers, strings, and more. With PROFINET, the vendor describes the data in the GSD file of their device and this gets mapped into the memory of the controller for access in the user application program.
Device Diagnostics
Device diagnostics are crucial as they help resolve automation problems quickly. Modbus TCP does not have device diagnostics, it only supports some message handling errors such as protocol communication timeout (message transfer error, device busy etc.). PROFINET has many diagnostic capabilities built into the protocol for process, device, or network errors. In addition, many PROFINET devices also support SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) and HTTP (web pages). And this allows further diagnostics for network statistics (network load, CRC errors, etc.). Finally, PROFINET specifies the use of LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol) for further network diagnostics, such network topology. All of these combined make troubleshooting far easier and faster with a PROFINET network.
PROFINET has (more) features
PROFINET has many more features than Modbus, such as a process automation profile, peer to peer, functional safety (PROFIsafe), controller redundancy, shared device, fast startup, network, etc. Those features enhance the applications that you can achieve and future-proof the system. Also, PROFINET is working towards future goals such as easy integration with Industry 4.0, IIoT, TSN, APL, and OPC UA. On the contrary, according to their website, the Modbus organization is keeping Modbus TCP the way it is for simplicity reasons.
Conformance Testing
It is mandatory for PROFINET devices to be certified by a PROFINET International (PI) authorized test lab. Therefore, all devices meet the PROFINET standard functions and can inter-operate in the field easily. With Modbus TCP the certification can be self-certified or the device can optionally be sent into a lab. The scope of the testing in PROFINET vs Modbus is very different and PROFINET testing is much more stringent, including a network load test and quality of performance.
Support
PROFINET is not only supported worldwide in many different languages by PI certified training centers, test labs, and competence centers, but there are over 1600 member companies using PROFINET and supporting the technology. With Modbus, there are 90 members with the primary backer being Schneider, 1 test lab, and zero training centers. Primary backers of PROFINET include Emerson, Siemens, Phoenix Contact, and many more. In addition, as of 2019 there are over 60 million PROFIBUS nodes and over 32 million PROFINET nodes already in the market.
PROFINET and Modbus
If needed, there are gateways available for communication between a PROFINET and Modbus TCP device or controller. There are multiple manufacturers that offer these solutions, and most of them have made it easy to map the data between the two systems.
Summary Table
To conclude our comparison, here is a summary table showing the main points:
| Technology | PROFINET | Modbus TCP |
|---|---|---|
| Ethernet IO | Y | Y |
| Motion Control | Y | N |
| Peer to Peer | Y | N |
| Safety | Y | N |
| Buses Integrated | many (including non PI networks), PROFIBUS, Interbus, ASI, DeviceNet, Foundation Fieldbus, Hart, etc. | Modbus |
| Communication Model | Provider-Consumer (allows full duplex) | Client Server (half duplex) |
| Real time Protocol options | IEEE 802.3 (layer 2) primary, UDP/IP option | TCP/IP |
| Jitter with IO | ++ (low), 1ms typical | -- (high), 100ms |
| Transmission type | Unicast Primary, Multicast optional | Unicast only |
| Network Management | DCP, DHCP option, SNMP, LLDP, topology options, naming | limited, no standard way, vendor specific |
| Comprehensive diagnostics | Y, application process, device, and network | N |
| Controller / Device redundancy | Y | N |
| Horizontal and Vertical Integration | Y, process, factory, and motion control for simple to complex applications | Y, process, limited factory for simple applications |
 Continue your education by completing a PROFINET Certified Network Engineer Course.
Continue your education by completing a PROFINET Certified Network Engineer Course.
These certification classes are intense, hands-on courses. You will learn how the underlying technology works from the application to the frame level. After passing both a practical and written exam, you become certified.
For more information, contact us or visit our website.